Curricula in Peppi
The principles of the curricula guides the preparation and implementation of curricula. Make sure to read the document before you start working on your curriculum.
The curriculum schedules and deadlines for each year are available on the intranet.
A curriculum is constructed as follows (see Figure 1):
- the description of the degree and the definitions of competence areas, i.e. the description of competences, are written in Teams.
- degree structure, syllabuses and classifications (incl. competence areas) to Peppi.
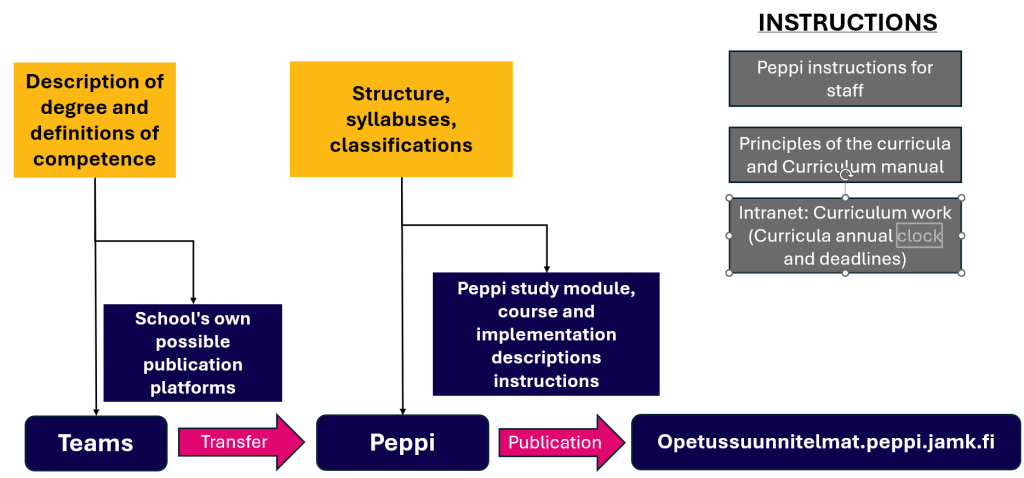
New degree: description and competence
Start creating a new degree curriculum by writing a description of the degree and its competence in Teams. The description of a degree programme consists of:
- key learning outcomes: what competence a student will achieve by completing the programme
- educational content and professional growth and know-how: how the accumulation of competence is expressed and evaluated as a student’s intended learning outcomes
- flexible implementation of studies
- working life-orientated learning
- career opportunities and employment
- qualifications
- further studies
- education planning: how regional and national foresight information has been used in the planning of the education and how planning has been carried out in cooperation with business and industry, students and other stakeholders
- responsible person: who is responsible for the degree programme.
The qualification description template and more detailed instructions are available in the Teams workspace titled Curriculum work.
- An administrative planner in Educational Development Services transfers the description texts and competences (competence areas) to Peppi.
- The description of a new degree taught in Finnish will be translated by Educational Development Services.
Stages of defining the competences of a degree
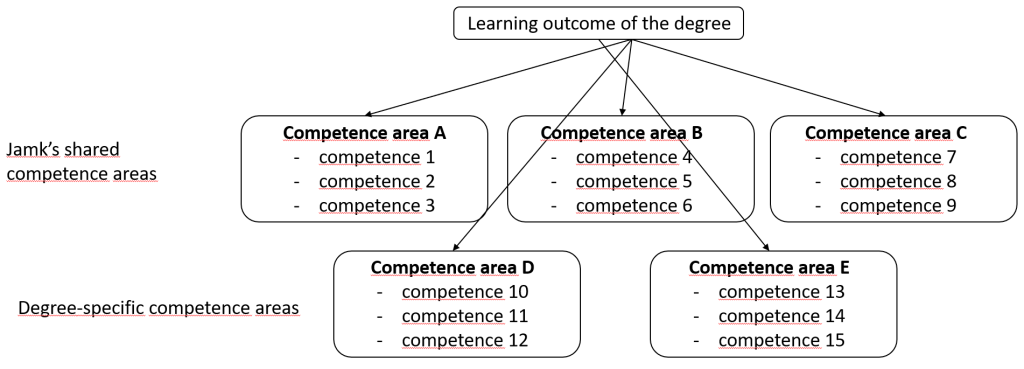
- Define the intended learning outcome of the degree in close collaboration with business and industry and possible other networks.
- Structure the intended learning outcome into degree-specific competence areas. Also keep Jamk’s shared competence areas in mind. In addition, accredited degree programmes may include European or international competence areas. The maximum recommended number of competence areas is 10.
- The competence areas are described as competences (Figure 2).
- Make sure that the competence areas and competences of degree programmes taught in Finnish are translated into English. The translations are done according to the degree programme’s instructions. The texts can also be sent to a translation service provider tendered by Jamk.
Updating a description (old degree programme)
For updating a curriculum, update the degree descriptions directly to Peppi in the Units > Degree programmes menu. Remember to update the English fields of a degree programme taught in English.
If competence areas are changed, they are always updated by sending the updated sections to an administrative planner in Educational Development Services (Finnish and English).
Curriculum: structure, syllabuses and classifications
The studies’ structure, scope, planned schedule and competences (classifications in Peppi) that will be accumulated during the degree programme are described in more detail in Peppi and published on the Curricula page. The structure of the studies consists of study modules and courses.
Study module
- Like a course, a study module is a structural part of a curriculum.
- A study module forms an independent entity made up of courses.
- Study modules can be based on different starting points. The starting point for a study module can be something like a phenomenon, a work entity, theme, core competence, etc.
- A description and learning outcomes are written for the study module, which enable the identification and recognition of the competence of the entire study module; studification as well. In addition, criteria for a study module are written when a study module contains non-compulsory courses.
- The learning outcome field of the study module is for describing the overall objective of the courses in the relevant competence area in a concise and clear manner.
- The objectives of a study module are defined in such a way that they are linked to the competence areas of the degree programme and/or common competence areas whose achievement is assessed as studies progress. The intended learning outcomes of the study module support the accumulation of a student’s overall competence.
- The minimum scope of a study module is 15 credits, consisting of at least two courses.
Course
- Principles and code instructions for creating courses are available Peppi instructions for staff.
- Course descriptions are prepared: learning outcomes, content and assessment criteria.
- The necessary course material is planned in cooperation with the library.
- The courses in the bachelor’s degree programmes are divided into basic studies, professional studies, elective studies, practical training and thesis. In master’s degree programmes, studies are divided into advanced professional studies, master’s thesis, and elective studies. This is done in Peppi with the structuralisation tools (‘Structure of the studies’ classification).
Syllabuses
- The syllabuses are recommendations on when and in what order students should complete the courses included in the degree.
- Determine the year and period for each course.
- Schedule studies evenly throughout the degree (30 credits / semester).
- Note: the autumn semester has fewer working weeks than the spring semester, which is important to take into account in the schedule. In a bachelor’s degree programme, a balanced workload means that you should plan up to 25 credits (17 weeks = 40 h/week) for the autumn and up to 30 credits (19 weeks = about 43 h/week) for the spring.
- Students need to have the option to take summer studies for at least 5 credits of compulsory or elective studies included in their degree, for example at the turn of May or June or in August.
Classifications (e.g. competence areas)
You can use the Peppi classification tool to classify courses in as many ways as necessary. At Jamk, courses are classified by the type of studies and by competence areas. Below is a description of how competence areas are used in classification.
- The competence areas and competences are created in Peppi by an administrative planner in Educational Development Services.
- Attach competence areas to courses with the classification tool. Note: competence areas are not automatically transferred to the course description and have to be kept up to date manually.
- In addition to degree-specific competence areas, attach degree programmes’ common competence areas to your degree programme.
- The development of degree-specific competence areas should be spread out over the duration of the degree.
- Degree programmes’ shared competence areas also have to be accumulated in professional studies (bachelor’s degree) or advanced professional studies (master’s degree).
- Note: Students can view the structures only through the Curriculum website.
Review, approval and publication of curricula
The student is entitled to complete studies leading to a bachelor’s degree or a master’s degree in line with the curriculum of the relevant degree programme (Degree Regulations, section 13).
The curriculum from the previous year is copied by the Educational development services to serve as the basis for the following year’s curriculum. If no changes are made, it can be published as is. If changes are made, the process continues as follows:
- The review of the contents of a curriculum is carried out by the Head of Department responsible for the degree programme or a person appointed by the Head of Department. The curriculum is submitted to the school management team before it is approved by the Student Affairs Board.
- The curriculum development team coordinates the curricula reviews, after which the curricula are published. The Student Affairs Board approves the curricula.
- New courses have to undergo linguistic and content reviews. The reviewers are noted in the course review section in Peppi. The review cannot be done by the person who is responsible for writing the description.
Note: Changes to the curriculum structure cannot be made after students have started studies in accordance with said structure.
Course and study module descriptions
For degree programmes taught in Finnish, descriptions are written in Finnish and translated into English. Similarly, for degree programmes taught in English, the description is written in English and translated into Finnish. Translations are produced according to the degree programme’s instructions. If necessary, translations can be ordered from a translation service provider tendered by Jamk.
You can write the descriptions of courses and study modules either directly to Peppi or
- study module descriptions can first be written in Teams and transferred from there to Peppi in accordance with the practices of the degree programme.
- course descriptions are written in Peppi.
Instructions for writing course descriptions are available in the Peppi instructions for staff.
The descriptions of new study modules and courses become publicly available after the structure they are attached to is published.
How a curriculum connects to students’ personal learning plans
A student’s personal study plan, or PLP, in Peppi is initially set as the curriculum of the degree and academic year to which the student’s group is attached in Peppi. Once a student’s personal learning plan has been initialised (after they have been admitted as a student), changes to the curriculum no longer affect the student’s personal learning plan and have to be submitted to it manually if necessary.
Links
- The principles of the curricula (For Students web pages)
- Curricula annual clock (Elmo intranet)
- Curricula work at Teams
- Instructions for ordering translation services
- Peppi Instructions for Staff
- Degree Regulations (For Students web pages)
- Publised curricula (Peppi, curricula)
- Principles for creating a course at Jamk and code instructions (Help)
- Course description instruction (Help)
Anne Luukkonen 23.2.2026